Multifamily buildings, including both dwelling units and common use areas, that comply with the prescriptive standards shall be designed, constructed, and equipped to meet all of the requirements for the appropriate Climate Zone shown in Table 170.2-A. In Table 170.2-A, a NA (not allowed) means that feature is not permitted in a particular Climate Zone and a NR (no requirement) means that there is no prescriptive requirement for that feature in a particular Climate Zone. Installed components shall meet the following requirements:
Note: Demising walls are not exterior walls, and therefore demising wall area is not part of the gross exterior wall area, and fenestration in demising walls is not part of the fenestration area limitation.
Vertical fenestration in demising walls between conditioned and unconditioned spaces is only required to comply with the area-weighted average U-factor requirement in Table 170.2-A.
Exception 1 to Section 170.2(a)3Aii: For each dwelling unit, up to 3 square feet of new glazing area installed in doors shall not be required to meet the U-factor and RSHGC requirements of Table 170.2-A.
Exception 2 to Section 170.2(a)3Aii: For fenestration containing chromogenic type glazing:
-
The lower-rated labeled U-factor and SHGC shall be used with automatic controls to modulate the amount of solar gain and light transmitted into the space in multiple steps in response to daylight levels or solar intensity;
-
Chromogenic glazing shall be considered separately from other fenestration; and
-
Area-weighted averaging with other fenestration that is not chromatic shall not be permitted and shall be determined in accordance with Section 110.6(a).
Exception 3 to Section 170.2(a)3Aii: For dwelling units containing unrated site-built fenestration that meets the maximum area restriction, the U-factor and SHGC can be determined in accordance with the Nonresidential Reference Appendix NA6 or using default values in Table 110.6-A and Table 110.6-B.
Exception 4 to Section 170.2(a)3Aii: Fenestration in dwelling units of buildings that are three habitable stories or fewer in climate zones 1, 3, 5, and 16, are not required to comply with the RSHGC requirements.
Exception 5 to Section 170.2(a)3Aii: Fenestration in dwelling units of buildings that are three habitable stories or fewer is not required to comply with the VT requirements.
For the purposes of this paragraph, the RSHGC of a vertical window is:
Exception 1 to Section 170.2(a)3Aiiib: An area-weighted average Relative Solar Heat Gain Coefficient of 0.56 or less shall be used for windows:
-
That are in the first story of exterior walls that form a display perimeter; and
-
For which codes restrict the use of overhangs to shade the windows.
Exception 2 to Section 170.2(a)3Aiiib: For vertical glazing containing chromogenic type glazing:
-
the lower-rate labeled RSHGC shall be used with automatic controls to modulate the amount of heat flow into the space in multiple steps in response to daylight levels or solar intensity; and
-
chromogenic glazing shall be considered separately from other glazing; and
-
area-weighted averaging with other glazing that is not chromogenic shall not be permitted.
Note: Demising walls are not exterior walls, and therefore fenestration in demising walls are not subject to SHGC requirements.
RSHGC = SHGC × [1 + a × (2.72-PF– 1) × (sin(b × Az) + c)]
Where:
a | b | c | |
Overhang | 0.150 | 0.008727 | 5.67 |
Exterior Horizontal Slat | 0.144 | 0.008727 | 5.13 |
RSHGC = Relative Solar Heat Gain Coefficient.
SHGC = Solar Heat Gain Coefficient of the vertical fenestration.
Az = Azimuth of the vertical fenestration I degrees.
PF = Projection factor as calculated by Equation 140.3-D.
Exception 1 to Section 170.2(a)3Aiv: When the window’s primary and secondary sidelit daylit zones are completely overlapped by one or more skylit daylit zones, then the window need not comply with Section 170.2(a)3Aivw.
Exception 2 to Section 170.2(a)3Aiv: If the window’s VT is not within the scope of NFRC 200,or ASTM E972, then the VT shall be calculated according to Reference Nonresidential Append ix NA6.
Exception 3 to Section 170.2(a)3Aiv: For vertical windows containing chromogenic type glazing:
-
The higher rated labeled VT shall be used with automatic controls to modulate the amount of light transmitted into the space in multiple steps in response to daylight levels or solar intensity;
-
Chromogenic glazing shall be considered separately from other glazing; and
-
Area-weighted averaging with other glazing that is not chromogenic shall not be permitted.
Exception 4 to Section 170.2(a)3iv: Fenestration in dwelling units of buildings that is three habitable stories or fewer are not required to comply with the VT requirements.
Note: Demising walls are not exterior walls, and therefore windows in demising walls are not subject to VT requirements.
VT ≥ 0.11/ WWR
Where:
WWR = Window Wall Ratio, the ratio of (i) the total window area of the entire building to (ii) the total gross exterior wall area of the entire building. If the WWR is greater than 0.40, then 0.40 shall be used as the value for WWR in Equation 170.2-B.
VT = Visible Transmittance of framed window.
Exception 1 to Section 170.2(a)3Bi: Buildings with an atrium over 55 feet high shall have a skylight area no greater than 10 percent of the gross exterior roof area.
Exception 2 to Section 170.2(a)3Bii: For each dwelling unit up to 16 square feet of new skylight area with a maximum U-factor of 0.55 and a maximum SHGC of 0.30.
Exception to Sections 170.2(a)3Bii and 170.2(a)3Biii: For skylights containing chromogenic type glazing:
Exception to Section 170.2(a)3Biv: Skylights designed and installed to exclude direct sunlight entering the occupied space by the use of fixed or automated baffles or the geometry of the skylight and light well.
Multifamily | Climate Zone | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |||||||||||
Roof/Ceiling | Option B (meets §170.2(a)1Bii) | Below Roof Deck Insulation1,2 (With Air Space) | NR | NR | NR | R19 | NR | NR | NR | R19 | R19 | R13 | R19 | R19 | R19 | R19 | R19 | R13 | ||||||||
Ceiling Insulation | R 38 | R 38 | R 30 | R 38 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | ||||||||||
Radiant Barrier | NR | REQ | REQ | NR | REQ | REQ | REQ | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||||||
Low-sloped | Aged Solar Reflectance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.63 | NR | 0.63 | NR | |||||||||
Thermal Emittance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.75 | NR | 0.75 | NR | ||||||||||
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 75 | NR | 75 | NR | ||||||||||
Steep-sloped | Aged Solar Reflectance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | NR | |||||||||
Thermal Emittance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0. 75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | NR | ||||||||||
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | NR | ||||||||||
Option C (meets §170.2(a)1Biii) | Ceiling Insulation | R 38 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 30 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | R 38 | |||||||||
Radiant Barrier | NR | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | REQ | NR | ||||||||||
Low-sloped | Aged Solar Reflectance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.63 | NR | 0.63 | NR | |||||||||
Thermal Emittance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.75 | NR | 0.75 | NR | ||||||||||
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 75 | NR | 75 | NR | ||||||||||
Steep-sloped | Aged Solar Reflectance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | NR | |||||||||
Thermal Emittance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0. 75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | NR | ||||||||||
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | NR | ||||||||||
Option D ( Non Attic Roof) | Metal Building U-factor | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | |||||||||
Wood Framed and Other U-factor | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.034 | 0.028 | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.039 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.028 | ||||||||||
Low-sloped | Aged Solar Reflectance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | NR | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | NR | |||||||||
Thermal Emittance | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | NR | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | NR | ||||||||||
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 75 | 75 | 75 | NR | 75 | 75 | 75 | NR | ||||||||||
Steep-sloped | Aged Solar Reflectance | NR | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | NR | |||||||||
Thermal Emittance | NR | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0. 75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | NR | ||||||||||
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) | NR | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | NR | ||||||||||
Walls | Metal-Building, any fire rating | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 0.057 | |||||||||
Framed (wood, metal) and other >1hr fire rating | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.065 | 0.065 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.051 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | ||||||||||
Framed (wood, metal) and other, ≤1hr fire rating 3 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.065 | 0.065 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | ||||||||||
Mass Light 4,5 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.077 R 13 | U 0.059 R 17 | ||||||||||
Mass Heavy | 0.253 | 0.650 | 0.650 | 0.650 | 0.650 | 0.690 | 0.690 | 0.690 | 0.690 | 0.650 | 0.184 | 0.253 | 0.211 | 0.184 | 0.184 | 0.160 | ||||||||||
Floors/Soffits | Slab Perimeter, Three Habitable Stories or less | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | U 0.58 R 7.0 | |||||||||
Wood Framed | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | U 0.037 R 19 | ||||||||||
Raised Mass | U 0.092 R 8.0 | U 0.092 R 8.0 | U 0.269 R 0 | U 0.269 R 0 | U-0.269 R 0 | U 0.269 R 0 | U 0.269 R 0 | U 0.269 R 0 | U 0.269 R 0 | U 0.269 R 0 | U 0.092 R 8.0 | U 0.138 R 4.0 | U 0.092 R 8.0 | U 0.092 R 8.0 | U 0.138 R 4.0 | U 0.092 R 8.0 | ||||||||||
Other | 0.048 | 0.039 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.039 | 0.071 | 0.071 | 0.039 | 0.039 | 0.039 | ||||||||||
Quality Insulation Installation (QII) for buildings up to three habitable stories | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | NR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||||||
Fenestration | Curtain Wall/ Storefront | Maximum U-factor | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.38 | ||||||||
Maximum RSHGC, three or fewer habitable stories | NR | 0.26 | NR | 0.26 | NR | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.26 | NR | ||||||||||
Maximum RSHGC, four or more habitable stories | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.25 | ||||||||||
Minimum VT, four or more habitable stories | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | ||||||||||
NAFS 2017 Performance Class AW 5 | Maximum U-factor | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.38 | |||||||||
Maximum RSHGC, three or less habitable stories | NR | 0.24 | NR | 0.24 | NR | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | NR | ||||||||||
Maximum RSHGC, four or more habitable stories | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | ||||||||||
Minimum VT, four or more habitable stories | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | ||||||||||
All Other Fenestration | Maximum U-factor | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | |||||||||
Maximum RSHGC, three or less habitable stories | NR | 0.23 | NR | 0.23 | NR | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | NR | ||||||||||
Maximum RSHGC, four or more habitable stories | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | ||||||||||
Maximum Window to Floor Ratio | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | ||||||||||
Maximum Window to Wall Ratio | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | 40% | ||||||||||
Maximum Skylight Roof Ratio | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | ||||||||||
Exterior Doors 6 | Maximum U-factor | Dwelling Unit Entry | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | ||||||||
Common Use Area Entry Non-Swinging | 0.50 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 0.50 | ||||||||||
Common Use Area Entry Swinging | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | ||||||||||
Footnote requirements to TABLE 170.2-A: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1. Install the specified R-value with an air space present between the roofing and the roof deck. Such as standard installation of concrete or clay tile. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2. R-values shown for below roof deck insulation are for wood-frame construction with insulation installed between the framing members. Alternatives including insulation above rafters or above roof deck shall comply with the performance standards . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3. Assembly U-factors for exterior framed walls can be met with cavity insulation alone or with continuous insulation alone, or with both cavity and continuous insulation that results in an assembly U-factor equal to or less than the U-factor shown. Use Reference Joint Appendices JA4 Table 4.3.1, 4.3.1(a), or Table 4.3.4 to determine alternative insulation products to be less than or equal to the required maximum U-factor. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4. Mass wall has a heat capacity greater than or equal to 7.0 Btu/h-ft 2 . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5. Product must be certified to meet the North American Fenestration Standard/Specification for an Architectural Window (AW). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6. Glazed doors must meet the fenestration requirements | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)3BiaI: Systems that cannot conform to the specifications for hole location in Reference Residential Appendix Figure RA3.2-1, shall not be required to provide holes as described in Figure RA3.2-1.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)3BiaII: Standard ducted systems without zoning dampers may comply with the minimum airflow rate by meeting the applicable requirements in Table 160.3-A and Table 160.3-B as confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the procedures in Reference Residential Appendix Sections RA3.1.4.4 and RA3.1.4.5. The design clean-filter pressure drop requirements of Section 160.2(b)1D for the system air filter device(s) shall conform to the requirements given in Table 160.3-A and Table 160.3-B.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)3BiaIII: When the outdoor temperature is less than 55 degrees F and the installer utilizes the weigh-in charging procedure in Reference Residential Appendix Section RA3.2.3.1 to verify the refrigerant charge, the installer may elect to utilize the HERS Rater verification procedure in Reference Residential Appendix RA3.2.3.2. If the HERS Rater verification procedure in Section RA3.2.3.2 is used for compliance, the system's thermostat shall conform to the specifications in Section 110.12. Ducted systems shall comply with the minimum system airflow rate requirement in Section 170.2(c)3BiaII.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)3Bi: Packaged systems for which the manufacturer has verified correct system refrigerant charge prior to shipment from the factory are not required to have refrigerant charge confirmed through field verification and diagnostic testing. The installer of these packaged systems shall certify that the packaged system was pre-charged at the factory and has not been altered in a way that would affect the charge. Ducted systems shall comply with minimum system airflow rate requirement in 170.2(c)3Bib, provided that the system is of a type that can be verified using the procedure specified in RA3.3 or an approved alternative in RA1.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)3Bi: The HERS Rater field verification and HERS Provider data registry requirements of Reference Residential Appendix RA2 and RA3 are not required for multifamily dwelling units in buildings four habitable stories and greater. The installer shall certify that diagnostic testing was performed in accordance with the applicable procedures.
NOTE: Gas heating appliances installed in conditioned spaces must meet the combustion air requirements of the California Mechanical Code Chapter 7, as applicable.
These measures shall be confirmed through HERS field verification in accordance with the procedures in RA3.7.4.4 for buildings with three habitable stories or less, or the procedures in NA2.2.4.1.5 for buildings with four or more habitable stories.
These measures shall be filed verified in accordance with NA7.18.4.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)3B: The HERS Rater field verification and HERS Provider data registry requirements of Reference Residential Appendix RA2 and RA3 are not required for multifamily dwelling units in buildings four habitable stories and greater. The installer shall certify that diagnostic testing was performed in accordance with the applicable procedures.
FPAadj= Qcomp/Qsys X FPAcomp
Where:
FPAadj = The correct/ed fan power allowance for the component in w/cfm
Qcomp = The airflow through component in cfm
Qsys = The fan system airflow in cfm
FPAcomp = The fan power allowance of the component from Table 170.2-B or Table 170.2-C
|
Multi-Zone VAV Systems ≤5,000 cfm
|
Multi-Zone VAV Systems >5,000 and ≤10,000 cfm
|
Multi-Zone VAV Systems >10,000 cfm
|
All Other Fan Systems ≤5,000 cfm
|
All Other Fan Systems >5,000 and ≤10,000 cfm
|
All Other Fan Systems >10,000 cfm
| |||
|
Supply System Base Allowance for AHU Serving Spaces < 6 Floors Away.
|
0.395
|
0.453
|
0.413
|
0.232
|
0.256
|
0.236
| ||
|
Supply System Base Allowance for AHU Serving Spaces > 6 Floors Away
|
0.508
|
0.548
|
0.501
|
0.349
|
0.356
|
0.325
| ||
|
MERV 13 to MERV 16 Filter Upstream of Thermal Conditioning Equipment (two times the clean filter pressure drop)2
|
0.136
|
0.114
|
0.105
|
0.139
|
0.120
|
0.107
| ||
|
MERV 13 to MERV 16 Final Filter Downstream of Thermal Conditioning Equipment. (two times the clean filter pressure drop)2
|
0.225
|
0.188
|
0.176
|
0.231
|
0.197
|
0.177
| ||
|
Filtration Allowance for > Merv 16 or HEPA Filter (two times the clean filter pressure drop)2
|
0.335
|
0.280
|
0.265
|
0.342
|
0.292
|
0.264
| ||
|
Central Hydronic Heating Coil Allowance
|
0.046
|
0.048
|
0.052
|
0.046
|
0.050
|
0.054
| ||
|
Electric Heat Allowance
|
0.046
|
0.038
|
0.035
|
0.046
|
0.040
|
0.036
| ||
|
Gas Heat Allowance
|
0.069
|
0.057
|
0.070
|
0.058
|
0.060
|
0.072
| ||
|
Hydronic/DX Cooling Coil, or Heat Pump Coil (wet) Allowance
|
0.135
|
0.114
|
0.105
|
0.139
|
0.120
|
0.107
| ||
|
Solid or Liquid Desiccant System Allowance
|
0.157
|
0.132
|
0.123
|
0.163
|
0.139
|
0.124
| ||
|
Reheat Coil for Dehumidification Allowance
|
0.045
|
0.038
|
0.035
|
0.046
|
0.040
|
0.036
| ||
|
Allowance for evaporative humidifier/cooler in series with a cooling coil. Value shown is allowed watts/cfm per 1.0 in. wg. Determine pressure loss (in. wg) at 400 fpm or maximum velocity allowed by the manufacturer, whichever is less. [Calculation required, see note 4]
|
0.224
|
0.188
|
0.176
|
0.231
|
0.197
|
0.177
| ||
|
Allowance for 100% outdoor air system meeting the requirements of Note 5.
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.070
|
0.100
|
0.107
| ||
|
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.50 ≤ ERR <0.55 6
|
0.135
|
0.114
|
0.105
|
0.139
|
0.120
|
0.107
| ||
|
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.55 ≤ ERR <0.60 6
|
0.160
|
0.134
|
0.124
|
0.165
|
0.141
|
0.126
| ||
|
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.60 ≤ ERR <0.65 6
|
0.184
|
0.155
|
0.144
|
0.190
|
0.163
|
0.146
| ||
|
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.65 ≤ ERR <0.70 6
|
0.208
|
0.175
|
0.163
|
0.215
|
0.184
|
0.165
| ||
|
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.70 ≤ ERR <0.75 6
|
0.232
|
0.196
|
0.183
|
0.240
|
0.205
|
0.184
| ||
|
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.75 ≤ ERR <0.80 6
|
0.257
|
0.216
|
0.202
|
0.264
|
0.226
|
0.203
| ||
|
Energy Recovery Allowance for ERR ≥ 0.80 6
|
0.281
|
0.236
|
0.222
|
0.289
|
0.247
|
0.222
| ||
|
Coil Runaround Loop
|
0.135
|
0.114
|
0.105
|
0.139
|
0.120
|
0.107
| ||
|
Allowance for gas phase filtration required by code or accredited standard. Value shown is allowed w/cfm per 1.0 in. wg air pressure drop. [Calculation required, see note 4]
|
0.224
|
0.188
|
0.176
|
0.231
|
0.197
|
0.177
| ||
|
Economizer Return Damper
|
0.045
|
0.038
|
0.035
|
0.046
|
0.040
|
0.036
| ||
|
Air Blender Allowance
|
0.045
|
0.038
|
0.035
|
0.046
|
0.040
|
0.036
| ||
|
Allowance for sound attenuation section [fans serving spaces with design background noise goals below NC35].
|
0.034
|
0.029
|
0.026
|
0.035
|
0.030
|
0.027
| ||
|
Deduction for systems that feed a terminal unit with a fan with electrical input power < 1kW.
|
-0.100
|
-0.100
|
-0.100
|
-0.100
|
-0.100
|
-0.100
| ||
|
Low-turndown single-zone VAV fan systems meeting the requirements in note 7.
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
0.000
|
.070
|
0.100
|
0.089
| ||
|
Footnote to TABLE 170.2-B
1. See FAN SYSTEM, MULTI-ZONE VARIABLE AIR VOLUME (VAV) in definition a Multi-Zone VAV System. 2. Filter fan power allowance can only be counted once per fan system. 3. RESERVED. 4. Power allowance requires further calculation by multiplying the actual in. wg . of the device/ component by the watts/ cfm in Table 170.2-B. 5. The 100% outdoor air system must serve 3 or more HVAC zones and airflow during non-economizer operating periods must not exceed 135% of minimum requirements in Section 120.1(c)3 . 6. Energy Recovery Ratio (ERR) calculated per ANSI/ASHRAE 84-2020. 7. A low-turndown single-zone VAV fan system must be capable of and configured to reduce airflow to 50 percent of design airflow and use no more than 30 percent of the design wattage at that airflow. No more than 10 percent of the design load served by the equipment shall have fixed loads. | ||||||||
Multi-Zone VAV Systems ≤5,000 cfm1 | Multi-Zone VAV Systems >5,000 and ≤10,000 cfm1 | Multi-Zone VAV Systems >10,000 cfm1 | All Other Fan Systems ≤5,000 cfm | All Other Fan Systems >5,000 and ≤10,000 cfm | All Other Fan Systems >10,000 cfm | |
Exhaust System Base Allowance | 0.221 | 0.246 | 0.236 | 0.186 | 0.184 | 0.190 |
Filter (any MERV value)2 | 0.046 | 0.041 | 0.036 | 0.046 | 0.041 | 0.035 |
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.50 ≤ ERR <0.55 3 | 0.139 | 0.120 | 0.107 | 0.139 | 0.123 | 0.109 |
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.55 ≤ ERR <0.60 3 | 0.165 | 0.142 | 0.126 | 0.165 | 0.144 | 0.128 |
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.60 ≤ ERR <0.65 3 | 0.190 | 0.163 | 0.146 | 0.191 | 0.166 | 0.148 |
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.65 ≤ ERR <0.70 3 | 0.215 | 0.184 | 0.165 | 0.216 | 0.188 | 0.167 |
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.70 ≤ ERR <0.75 3 | 0.240 | 0.206 | 0.184 | 0.241 | 0.209 | 0.186 |
Energy Recovery Allowance for 0.75 ≤ ERR <0.80 3 | 0.265 | 0.227 | 0.203 | 0.266 | 0.231 | 0.205 |
Energy Recovery Allowance for ERR ≥ 0.80 3 | 0.289 | 0.248 | 0.222 | 0.291 | 0.252 | 0.225 |
Coil Runaround Loop | 0.139 | 0.120 | 0.107 | 0.139 | 0.123 | 0.109 |
Return or exhaust systems required by code or accreditation standards to be fully ducted, or systems required to maintain air pressure differentials between adjacent rooms | 0.116 | 0.100 | 0.089 | 0.116 | 0.102 | 0.091 |
Return and/or exhaust airflow control devices required for space pressurization control | 0.116 | 0.100 | 0.089 | 0.116 | 0.102 | 0.091 |
Laboratory and vivarium exhaust systems in high-rise buildings for vertical duct exceeding 75 ft. Value shown is allowed w/cfm per 0.25 in. wg for each 100 feet exceeding 75 feet. [Calculation required, see note 4] | 0.058 | 0.051 | 0.045 | 0.058 | 0.052 | 0.046 |
Biosafety cabinet. Value shown is allowed w/cfm per 1.0 in. wg air pressure drop. [Calculation required, see note 4] | 0.231 | 0.198 | 0.177 | 0.232 | 0.202 | 0.179 |
Exhaust filters, scrubbers, or other exhaust treatment required by code or standard. Value shown is allowed w/cfm per 1.0 in. wg air pressure drop. [Calculation required, see note 4] | 0.231 | 0.198 | 0.177 | 0.232 | 0.202 | 0.179 |
Sound attenuation section [Fans serving spaces with design background noise goals below NC35.] | 0.035 | 0.030 | 0.027 | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.028 |
Footnote to TABLE 170.2-C: 1. For requirements to be classified as a Multi-Zone VAV System see definition for Multi-Zone Variable Air Volume Fan System. 2. Filter pressure loss can only be counted once per fan system. 3. Energy Recovery Ratio (ERR) calculated per ANSI/ASHRAE 84-2020. 4. Power allowance requires further calculation, multiplying the actual pressure drop (in. wg .) of the device/ component by the watts/cfm in the Table 170.2-C | ||||||
Altitude (ft) | Correction factor |
<3,000 | 1.000 |
≥3,000 and <4,000 | 0.896 |
≥4,000 and <5,000 | 0.864 |
≥5,000 and <6,000 | 0.832 |
≥6,000 | 0.801 |
Motor Nameplate HP | Default Fan kWdesign with variable speed drive (Fan kWdesign ) | Default Fan kWdesign without variable speed drive (Fan kWdesign ) |
<1 | 0.96 | 0.89 |
≥1 and <1.5 | 1.38 | 1.29 |
≥1.5 and <2 | 1.84 | 1.72 |
≥2 and <3 | 2.73 | 2.57 |
≥3 and <5 | 4.38 | 4.17 |
≥5 and <7.5 | 6.43 | 6.15 |
≥7.5 and <10 | 8.46 | 8.13 |
≥10 and <15 | 12.47 | 12.03 |
≥15 and <20 | 16.55 | 16.04 |
≥20 and <25 | 20.58 | 19.92 |
≥25 and <30 | 24.59 | 23.77 |
≥30 and <40 | 32.74 | 31.70 |
≥40 and <50 | 40.71 | 39.46 |
≥50 and <60 | 48.50 | 47.10 |
≥60 and <75 | 60.45 | 58.87 |
≥75 and ≤100 | 80.40 | 78.17 |
Footnote to TABLE 170.2-E: 1. This table cannot be used for Motor Nameplate Horsepower values greater than 100. 2. This table is to be used only with motors with a service factor ≤1.15. If the service factor is not provided, this table may not be used. | ||
- 50 percent of the peak primary airflow; or
- The design zone outdoor airflow rate as specified by Section 160.2(c)3.
- 30 percent of the peak primary airflow; or
- The design zone outdoor airflow rate as specified by Section 160.2(c)3.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4B: Zones with special pressurization relationships or cross-contamination control needs.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4B: Zones served by space-conditioning systems in which at least 75 percent of the energy for reheating, or providing warm air in mixing systems, is provided from a site-recovered or site-solar energy source.
EXCEPTION 3 to Section 170.2(c)4B: Zones in which specific humidity levels are required to satisfy exempt process loads. Computer rooms or other spaces where the only process load is from IT equipment may not use this exception.
EXCEPTION 4 to Section 170.2(c)4B: Zones with a peak supply-air quantity of 300 cfm or less.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4Ci: Where special outside air filtration and treatment, for the reduction and treatment of unusual outdoor contaminants, makes compliance infeasible.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4Ci: Where the use of outdoor air for cooling will affect other systems, such as humidification or dehumidification, so as to increase overall building TDV energy use.
EXCEPTION 3 to Section 170.2(c)4Ci: Systems serving dwelling units.
EXCEPTION 4 to Section 170.2(c)4Ci: Where comfort cooling systems have the cooling efficiency that meets or exceeds the cooling efficiency improvement requirements in Table 170.2-F.
EXCEPTION 5 to Section 170.2(c)4Ci: Fan systems primarily serving computer rooms. See Section 140.9(a) for computer room economizer requirements.
| Climate Zones | Total Building Chilled Water System Capacity, Minus Capacity of the Cooling units with Air Economizers | |
| Building Water-Cooled Chilled Water System | Air-Cooled Chilled Water Systems or District Chilled Water Systems | |
| 15 | ≥ 960,000 Btu/h (280 kW) | ≥ 1,250,000 Btu/h (365 kW) |
| 1-14 | ≥720,000 Btu/h (210 kW) | ≥940,000 Btu/h (275 kW) |
| 16 | ≥1,320,000 Btu/h (385 kW) | ≥1,720,000 Bu/h (505 kW) |
Climate Zone | Efficiency Improvement a |
1 | 70% |
2 | 65% |
3 | 65% |
4 | 65% |
5 | 70% |
6 | 30% |
7 | 30% |
8 | 30% |
9 | 30% |
10 | 30% |
11 | 30% |
12 | 30% |
13 | 30% |
14 | 30% |
15 | 30% |
16 | 70% |
Footnote to TABLE 170.2-F a If a unit is rated with an annualized or part-load metric, then to eliminate the required economizer, only the annualized or part-load minimum cooling efficiency of the unit must be increased by the percentage shown. If the unit is only rated with a full load metric, like EER or COP cooling, then that metric must be increased by the percentage shown. To determine the efficiency required to eliminate economizer, when the unit equipment efficiency is rated with an energy-input divided by work-output metric, the metric shall first be converted to COP prior to multiplying by the efficiency improvement percentage and then converted back to the rated metric. | |
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)4Ciia: Systems that provide 75 percent of the annual energy used for mechanical heating from site-recovered energy or a site-solar energy source.
Device Typea | Climate Zones | Required High Limit (Economizer Off When): | Required High Limit (Economizer Off When): |
Equationb | Description | ||
Fixed Dry Bulb | 1, 3, 5, 11-16 | TOA > 75°F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds 75°F |
Fixed Dry Bulb | 2, 4, 10 | TOA > 73°F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds 73°F |
Fixed Dry Bulb | 6, 8, 9 | TOA > 71°F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds 71°F |
Fixed Dry Bulb | 7 | TOA > 69°F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds 69°F |
Differential Dry Bulb | 1, 3, 5, 11-16 | TOA > TRA °F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds return air temperature |
Differential Dry Bulb | 2, 4, 10 | TOA > TRA -2°F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds return air temperature minus 2°F |
Differential Dry Bulb | 6, 8, 9 | TOA > TRA -4°F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds return air temperature minus 4°F |
Differential Dry Bulb | 7 | TOA > TRA -6°F | Outdoor air temperature exceeds return air temperature minus 6°F |
Fixed Enthalpyc + Fixed Drybulb | All | hOA > 28 Btu/ lbc or TOA > 75°F | Outdoor air enthalpy exceeds 28 Btu/ lb of dry air c or Outdoor air temperature exceeds 75°F |
Footnote to TABLE 170.2-G: a Only the high limit control devices listed are allowed to be used and at the setpoints listed. Others such as Dew Point, Fixed Enthalpy, Electronic Enthalpy, and Differential Enthalpy Controls, may not be used in any Climate Zone for compliance with Section 170.2(c)4Ci unless approval for use is provided by the Energy Commission Executive Director. b Devices with selectable (rather than adjustable) setpoints shall be capable of being set to within 2°F and 2 Btu/ lb of the setpoint listed. c At altitudes substantially different than sea level, the Fixed Enthalpy limit value shall be set to the enthalpy value at 75°F and 50% relative humidity. As an example, at approximately 6,000 foot elevation, the fixed enthalpy limit is approximately 30.7 Btu/lb. | |||
-
Drybulb and wetbulb temperatures accurate to ±2°F over the range of 40°F to 80°F;
-
Enthalpy accurate to ±3 Btu/lb over the range of 20 Btu/lb to 36 Btu/lb;
-
Relative humidity (RH) accurate to ±5 percent over the range of 20 percent to 80 percent RH;
Cooling Capacity | Minimum Number of Mechanical Cooling Stages | Minimum Compressor Displacement |
≥ 65,000 Btu/h and < 240,000 Btu/h | 3 stages | ≤ 35% full load |
≥ 240,000 Btu/h | 4 stages | ≤ 25% full load |
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4Fi: Heat rejection devices included as an integral part of the equipment listed in TABLE 110.2-A through TABLE 110.2-N
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4Fiii: Cooling towers that are ducted (inlet or discharge) or have an external sound trap that requires external static pressure capability.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4Fiii: Cooling towers that meet the energy efficiency requirement for propeller fan towers in Section 110.2, Table 110.2-F.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4Fv: Replacement of existing cooling towers that are inside an existing building or on an existing roof.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4Fv: Cooling towers serving buildings in Climate Zone 1 or 16.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4I: Systems that include no more than three control valves.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4I: Systems having a total pump system power less than or equal to 1.5 hp.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)4Iiv: Hydronic systems that use variable flow to reduce pumping energy in accordance with Section 170.2(c)4Ii.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4Ivi: Heating hot water systems.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4Ivi: Condenser water systems serving only water-cooled chillers.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)4Ivii: Where a system loop temperature optimization controller is used to determine the most efficient operating temperature based on real-time conditions of demand and capacity, dead bands of less than 20°F shall be allowed.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4M: Spaces that are required by applicable codes and standards to be maintained at a positive pressure differential relative to adjacent spaces.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4M: Spaces where the highest amount of transfer air that could be used for exhaust makeup may exceed the available transfer airflow rate and where the spaces have a required negative pressure relationship.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)4Ni: Systems installed for the sole purpose of providing makeup air for exhausting toxic fumes, flammable materials, paint, corrosive fumes, dust, dryer exhaust, or commercial kitchen hoods used for collecting and removing grease vapors and smoke.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)4Niii: Fans used for heating and cooling using less than 0.12 watts per cfm may operate when space temperatures are within the thermostat deadband to provide destratification and air mixing in the space.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(c)4Niv: Active chilled beam systems.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(c)4Niv: Sensible only cooling terminal units with pressure-independent variable-airflow regulating devices limiting the DOAS supply air to the greater of latent load or minimum ventilation requirements.
EXCEPTION 3 to Section 170.2(c)4Niv: Terminal heating or cooling units that comply with the low fan power allowance requirements in EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(c)4Niii.
|
% Outdoor Air at Full Design Airflow |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
|
≥10% and <20% |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
|
≥20% and <30% |
≥15,000 |
≥20,000 |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥18,500 |
≥18,500 |
≥18,500 |
≥18,500 |
≥18,500 |
≥18,500 |
|
≥30% and <40% |
≥13,000 |
≥15,000 |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥15,000 |
≥15,000 |
≥15,000 |
≥15,000 |
≥15,000 |
≥15,000 |
|
≥40% and <50% |
≥10,000 |
≥12,000 |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥22,000 |
≥10,000 |
≥10,000 |
≥10,000 |
≥10,000 |
≥10,000 |
≥10,000 |
|
≥50% and <60% |
≥9,000 |
≥10,000 |
NR |
≥18,500 |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥17,000 |
≥8,000 |
≥8,000 |
≥8,000 |
≥8,000 |
≥8,000 |
≥8,000 |
|
≥60% and <70% |
≥7,000 |
≥7,500 |
NR |
≥16,500 |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥20,000 |
≥15,000 |
≥7,000 |
≥7,000 |
≥7,000 |
≥7,000 |
≥7,000 |
≥7,000 |
|
≥70% and <80% |
≥6,500 |
≥7,000 |
NR |
≥15,000 |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥17,000 |
≥14,000 |
≥5,000 |
≥5,000 |
≥5,000 |
≥5,000 |
≥5,000 |
≥5,000 |
|
≥80% |
≥4,500 |
≥6,500 |
NR |
≥14,000 |
NR |
NR |
NR |
NR |
≥15,000 |
≥13,000 |
≥2,000 |
≥2,000 |
≥2,000 |
≥2,000 |
≥2,000 |
≥2,000 |
Footnotes to TABLE 170.2-I:
1. Flow rates in TABLE 140.4-G represent the design supply fan airflow rate in CFM.
2. For a DOAS unit providing outdoor air to another space-conditioning system, the full design supply fan airflow rate shall be the total airflow of only the DOAS unit.
% Outdoor Air at Full Design Airflow | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
≥10% and <20% | ≥10,000 | ≥10,000 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ≥40,000 | ≥40,000 | ≥20,000 | ≥10,000 | ≥10,000 | ≥10,000 | ≥10,000 |
≥20% and <30% | ≥2,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥13,000 | ≥9,000 | ≥9,000 | NR | NR | NR | NR | ≥15,000 | ≥15,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥5,000 |
≥30% and <40% | ≥2,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥10,000 | ≥6,500 | ≥6,500 | NR | NR | NR | ≥15,000 | ≥7,500 | ≥7,500 | ≥3,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥3,000 |
≥40% and <50% | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥8,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥6,000 | NR | NR | NR | ≥12,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 |
≥50% and <60% | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥7,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥6,000 | NR | NR | ≥20,000 | ≥10,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 |
≥60% and <70% | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥6,000 | NR | NR | ≥18,000 | ≥9,000 | ≥4,000 | ≥4,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 |
≥70% and <80% | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥5,000 | NR | NR | ≥15,000 | ≥8,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 |
≥80% | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥6,000 | ≥5,000 | ≥5,000 | NR | NR | ≥12,000 | ≥7,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥3,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 | ≥2,000 |
Footnotes to TABLE 170.2-J:
1. Flow rates in TABLE 140.4-G represent the design supply fan airflow rate in CFM.
2. For a DOAS unit providing outdoor air to another space-conditioning system, the full design supply fan airflow rate shall be the total airflow of only the DOAS unit.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(d)3B: Buildings with eight or fewer dwelling units.
|
Multifamily
|
Climate Zone
| |||||||||||||||||
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
10
|
11
|
12
|
13
|
14
|
15
|
16
| |||
|
Unitary (serving one dwelling unit)
|
If Balanced Ventilation System 1
|
HRV or ERV Sensible Recovery Efficiency
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
|
HRV or ERV Fan Efficacy (W/cfm)
|
0.6
|
0.6
|
1.0
|
1.0
|
1.0
|
1.0
|
1.0
|
1.0
|
1.0
|
1.0
|
0.6
|
0.6
|
0.6
|
0.6
|
0.6
|
0.6
| ||
|
Non-HRV or Non-ERV Fan Efficacy (W/cfm)
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
0.4
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
| ||
|
If Heat Pump, HSPF 2 /HSPF2
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
| ||
|
If Dual-Fuel Heat Pump, AFUE
|
MIN
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
NA
|
MIN
| ||
|
Refrigerant Charge Verification or Fault Indicator Display
|
NR
|
REQ
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
NR
| ||
|
SEER/SEER2
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
|
MIN
| ||
|
Central (serving multiple dwelling units)
|
If Balanced Ventilation Systems 1
|
Sensible Recovery Efficiency or Effectiveness
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
0.67
|
|
Bypass Function
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
NR
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
| ||
|
Central System Air Handlers
|
Central Fan Integrated Ventilation System Fan Efficacy
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
|
REQ
| |
|
Duct Insulation
|
Ducts in Unconditioned Space
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-6
|
R-8
|
R-6
|
R-6
|
R-6
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-8
|
R-8
| |
|
Water Heating
|
All Buildings
|
System Shall meet Section 170.2(d)
| ||||||||||||||||
|
Footnotes to TABLE 170.2-K:
1. Requirements only apply when using Balanced Ventilation to meet 160.2(b)2Aivb . 2. HSPF means "heating seasonal performance factor." 3. A supplemental heating unit may be installed in a space served directly or indirectly by a primary heating system, provided that the unit thermal capacity does not exceed 2 kilowatts or 7,000 Btu/ hr and is controlled by a time-limiting device not exceeding 30 minutes. | ||||||||||||||||||
Common use area lighting shall meet the following requirements:
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(e): Common use areas providing shared provisions for living, eating, cooking, or sanitation to dwelling units that would otherwise lack these provisions may instead comply with Section 160.5(a).
The prescriptive limits on indoor lighting power are the smaller of the Actual and Allowed Indoor Lighting Power values determined in accordance with item i.
For compliance with Part 6 a Nonprogrammable Double-Throw Switch is an electrical switch commonly called a "single pole double throw" or "three-way" switch that is wired as a selector switch allowing one of two loads to be enabled. It can be a line voltage switch or a low voltage switch selecting between two relays. It cannot be overridden or changed in any manner that would permit both loads to operate simultaneously.
When used for determining PAFs for general lighting in offices, furniture mounted luminaires that comply with all of the following conditions shall qualify as permanently installed general lighting systems:
The allowed indoor lighting power allotment for general lighting for one area for which the Area Category Method was used may be increased up to the amount that the Allowed Indoor Lighting Power allotment for general lighting for another area using the Area Category Method or Tailored Method is decreased, except that such increases and decreases shall not be made between conditioned and unconditioned space.
-
the lighting power density listed in the “Allowed Additional Lighting LPD” column in Table 170.2-M, times the square feet of the primary function, or
-
the adjusted indoor lighting power of the applicable lighting.
|
TYPE OF CONTROL
|
TYPE OF AREA
|
FACTOR
|
|
1. Daylight Continuous Dimming plus OFF Control
|
Luminaires in skylit daylit zone or primary sidelit daylit zone
|
0.10
|
|
2. Occupant Sensing Controls in Office Spaces larger than 250 square feet
|
In open plan offices > 250 square feet: One sensor controlling an area that is: No larger than 125 square feet
|
0.30
|
|
In open plan offices > 250 square feet: One sensor controlling an area that is: From 126 to 250 square feet
|
0.20
| |
|
3.Institutional Tuning
|
Luminaires in non-daylit areas. Luminaires that qualify for other PAFs in this table may also qualify for this tuning PAF.
|
0.10
|
|
Luminaires in daylit areas. Luminaires that qualify for other PAFs in this table may also qualify for this tuning PAF.
|
0.05
| |
|
4. Demand Responsive Control
|
General lighting luminaires not in the scope of Section 110.12(c). Luminaires that qualify for other PAFs in this table may also qualify for this demand responsive control PAF
|
0.05
|
|
5. Clerestory Fenestration
|
Luminaires in daylit areas adjacent to the clerestory. Luminaires that qualify for daylight dimming plus OFF control may also qualify for this PAF.
|
0.05
|
|
6. Horizontal Slats
|
Luminaires in daylit areas adjacent to vertical fenestration with interior or exterior horizontal slats. Luminaires that qualify for daylight dimming plus OFF control may also qualify for this PAF.
|
0.05
|
|
7.Light Shelves
|
Luminaires in daylit areas adjacent to clerestory fenestration with interior or exterior light shelves. This PAF may be combined with the PAF for clerestory fenestration. Luminaires that qualify for daylight dimming plus OFF control may also qualify for this PAF
|
0.10
|
|
Footnote to TABLE 170.2-L:
a. To qualify for any of the Power Adjustment Factors in this table, the installation shall comply with the applicable requirements in Section 170.2(e)1Aii b. Only one PAF may be used for each qualifying luminaire unless combined below. c. Lighting controls that are required for compliance with Part 6 shall not be eligible for a PAF | ||
Primary Function Area | Allowed Lighting Power Density for General Lighting (W/ft2) | Additional Lighting Power Qualified Lighting Systems | Additional Lighting Power Additional Allowance (W/ft², unless noted otherwise) |
Storage | 0.45 | - | - |
Conference, Multipurpose and Meeting Area | 0.75 | Display/Decorative | 0.30 |
Copy Room | 0.50 | - | - |
Corridor Area | 0.40 | Decorative/Display | 0.25 |
Dining Area Bar/Lounge and Fine Dining | 0.45 | Display/Decorative | 0.35 |
Dining Area Cafeteria/Fast Food | 0.45 | Display/Decorative | 0.25 |
Dining Area Family and Leisure | 0.40 | Display/Decorative | 0.25 |
Health Care / Assisted Living Nurse’s Station | 0.75 | Tunable white or dim-to-warm 8 | 0.10 |
Health Care / Assisted Living Physical Therapy Room | 0.85 | Tunable white or dim-to-warm 8 | 0.10 |
Kitchen/Food Preparation Area | 0.95 | - | - |
Electrical, Mechanical, Telephone Rooms | 0.40 | Detailed Task Work 1 | 0.20 |
Exercise/Fitness Center and Gymnasium Area | 0.50 | - | - |
Lobby, Main Entry | 0.70 | Display/Decorative | 0.25 |
Locker Room | 0.45 | - | - |
Lounge, Breakroom, or Waiting Area | 0.55 | Display/Decorative | 0.25 |
Concourse and Atria Area | 0.60 | Display/Decorative | 0.25 |
Primary Function Area | Allowed Lighting Power Density for General Lighting (W/ft2) | Additional Lighting Power Qualified Lighting Systems | Additional Lighting Power Additional Allowance (W/ft², unless noted otherwise) | |
Office Area | > 250 square feet | 0.6 | Decorative/Display and Portable lighting for office areas 5 | 0.20 |
Office Area | ≤ 250 square feet | 0.6 5 | Decorative/Display and Portable lighting for office areas 5 | 0.20 |
Parking Garage Area | Parking Zone and Ramps | 0.10 | First ATM or Ticket Machine | 100 W |
Parking Garage Area | Parking Zone and Ramps | 0.10 | Additional ATM or Ticket machine | 50 W each |
Parking Garage Area | Daylight Adaptation Zones 3 | 1.00 | - | - |
Laundry Area | 0.45 | - | - | |
Restrooms | 0.65 | Decorative / Display | 0.35 | |
Stairwell | 0.60 | Decorative / Display | 0.35 | |
All other | 0.40 | - | - | |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Lobby, Main Entry | 0.85 | Display/Decorative | 0.30 |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Lobby, Main Entry | 0.85 | Transition Lighting OFF at night 7 | 0.95 |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Stairwell | 0.80 | Display/Decorative | 0.30 |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Corridor Area | 0.70 | Display/Decorative | 0.30 |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Lounge/Waiting Area | 0.80 | Display/Decorative | 0.30 |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Multipurpose Room | 0.85 | Display/Decorative | 0.30 |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Dining | 0.80 | Display/Decorative | 0.30 |
Aging Eye/Low-vision 6 | Restroom | 1.00 | Display/Decorative | 0.20 |
Footnotes for this table are listed below. | ||||
1. Detailed task work – Lighting provides high level of visual acuity required for activities with close attention to small elements and/or extreme close up work. | ||||
2. RESERVED | ||||
3. Daylight Adaptation Zones shall be no longer than 66 feet from the entrance to the parking garage. | ||||
4. RESERVED | ||||
5. Portable lighting in office areas includes under shelf or furniture-mounted supplemental task lighting qualifies when controlled by a time clock or an occupancy sensor. | ||||
6. Aging Eye/Low-vision areas can be documented as being designed to comply with the light levels in ANSI/IES RP-28 and are or will be licensed by local or state authorities for either senior long-term care, adult day care, senior support, and/or people with special visual needs. | ||||
7. Transition lighting OFF at night. Lighting power controlled by astronomical time clock or other control to shut off lighting at night. Additional LPD only applies to area within 30 feet of an exit. Not applicable to lighting in daylit zones. | ||||
8. Tunable white luminaires capable of color change greater than or equal to 2000K CCT, or dim-to-warm luminaires capable of color change greater than or equal to 500K CCT, connected to controls that allows color changing of the luminaires. | ||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
Primary Function Area | General Illumination Level (Lux) | Wall Lighting Power Density (W/ft) | Task Lighting Power Density (W/ft) | Allowed Decorative/ Special Effect Lighting Power Density (W/ft²) |
Conference, Multipurpose, and Meeting Center Areas | 300 | 2.00 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
Dining Areas | 200 | 1.25 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
Lobby, Main Entry | 200 | 3.50 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
Height in feet above finished floor and bottom of luminaire(s) | Wall Display Mounting Height Adjustment Factor |
< 10’-7” | 1.00 |
10’-7” to 14’-0” | 0.85 |
>14’-0” to 18’-0” | 0.75 |
> 18’-0” | 0.70 |
|
Determine the Room Cavity Ratio for Table 170.2-Q using one of the following equations.
|
|
Room cavity ratio for rectangular rooms
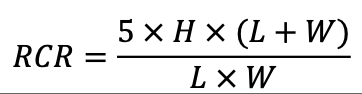 |
|
Room cavity ratio for irregular-shaped rooms
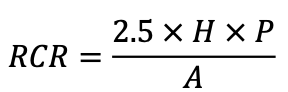 |
|
Where: L =Length of room; W = Width of room; H =Vertical distance from the work plane to the centerline of the lighting fixture; P = Perimeter of room, and A = Area of room |
|
General Illuminance Level (lux) a
|
RCR ≤ 2.0
|
RCR > 2.0 and ≤ 3.5
|
RCR > 3.5 and ≤ 7.0
|
RCR > 7.0
|
|
150
|
0.35
|
0.40
|
0.50
|
0.65
|
|
200
|
0.40
|
0.50
|
0.65
|
0.85
|
|
300
|
0.55
|
0.70
|
0.85
|
1.20
|
|
400
|
0.65
|
0.80
|
1.05
|
1.25
|
|
500
|
0.80
|
0.90
|
1.25
|
1.55
|
|
600
|
0.90
|
1.05
|
1.40
|
2.00
|
|
Footnotes to Table 170.2-Q
a Illuminance values from Column 2 of TABLE 170.2-N. b RCR values are calculated using applicable equations in TABLE 170.2-P. | ||||
|
Type of Power Allowance
|
Lighting Zone 0 2
|
Lighting Zone 1 2
|
Lighting Zone 2 2
|
Lighting Zone 3 2
|
Lighting Zone 4 2
|
|
Area Wattage Allowance (AWA)
|
No allowance 1
|
0.026 W/ft²
|
0.030 W/ft²
|
0.038 W/ft²
|
0.055 W/ft²
|
|
Initial Wattage Allowance (IWA)
|
No allowance 1
|
300 W
|
350 W
|
400 W
|
450 W
|
|
Footnotes to TABLE 170.2-R
| |||||
|
1 Continuous lighting is explicitly prohibited in Lighting Zone 0. A single luminaire of 15 Watts or less may be installed at an entrance to a parking area, trail head, fee payment kiosk, outhouse, or toilet facility, as required to provide safe navigation of the site infrastructure. Luminaires installed shall meet the maximum zonal lumen limits as specified in Section 160.5(c)1.
| |||||
|
2 Narrow band spectrum light sources with a dominant peak wavelength greater than 580 nm – as mandated by local, state, or federal agencies to minimize the impact on local, active professional astronomy or nocturnal habitat of specific local fauna – shall be allowed a 2.0 lighting power allowance multiplier.
| |||||
Lighting Application | Lighting Zone 0 | Lighting Zone 1 | Lighting Zone 2 | Lighting Zone 3 | Lighting Zone 4 |
WATTAGE ALLOWANCE PER APPLICATION. Use all that apply as appropriate. | |||||
Building Entrances or Exits. Allowance per door. Luminaires qualifying for this allowance shall be within 20 feet of the door | Not applicable | 9 watts | 15 watts | 19 watts | 21 watts |
Primary Entrances to Senior Care Facilities Allowance per primary entrance(s) only. Primary entrances shall provide access for the general public and shall not be used exclusively for staff or service personnel. This allowance shall be in addition to the building entrance or exit allowance above. Luminaires qualifying for this allowance shall be within 100 feet of the primary entrance. | Not applicable | 20 watts | 40 watts | 57 watts | 60 watts |
ATM Machine Lighting. Allowance per ATM machine. Luminaires qualifying for this allowance shall be within 50 feet of the dispenser. | Not applicable | 100 watts for first ATM machine, 35 watts for each additional ATM machine. | |||
WATTAGE ALLOWANCE PER HARDSCAPE AREA (W/ft²). May be used for any illuminated hardscape area on the site. | |||||
Hardscape Ornamental Lighting. Allowance for the total site illuminated hardscape area. Luminaires qualifying for this allowance shall be rated for 50 watts or less as determined in accordance with Section 160.5(b)1 and shall be post-top luminaires, lanterns, pendant luminaires, or chandeliers. | Not applicable | No Allowance | 0.007 W/ft2 | 0.013 W/ft2 | 0.019 W/ft2 |
WATTAGE ALLOWANCE PER SPECIFIC AREA (W/ft²). Use as appropriate provided that none of the following specific applications shall be used for the same area. | |||||
Building Facades. Only areas of building façade that are illuminated shall qualify for this allowance. Luminaires qualifying for this allowance shall be aimed at the façade and shall be capable of illuminating it without obstruction or interference by permanent building features or other objects. This allowance calculation shall not include portions of the building façades within 20 feet of residence bedroom windows. | Not applicable | No Allowance | 0.100 W/ft² | 0.170 W/ft² | 0.225 W/ft² |
Canopies and Tunnels. Allowance for the total area within the drip line of the canopy or inside the tunnel. Luminaires qualifying for this allowance shall be located under the canopy or tunnel. | Not applicable | 0.057 W/ft² | 0.137 W/ft² | 0.270 W/ft² | 0.370 W/ft² |
Student Pick-up/Drop-off zone. Allowance for the area of the student pick-up/drop-off zone, with or without canopy, for preschool through 12th grade school campuses. A student pick-up/drop off zone is a curbside, controlled traffic area on a school campus where students are picked-up and dropped off from vehicles. The allowed area shall be the smaller of the actual width or 25 feet, times the smaller of the actual length or 250 feet. Qualifying luminaires shall be within 2 mounting heights of the student pick-up/drop-off zone. | Not applicable | No Allowance | 0.056 W/ft² | 0.200 W/ft² | No Allowance |
Outdoor Dining. Allowance for the total illuminated hardscape of outdoor dining. Outdoor dining areas are hardscape areas used to serve and consume food and beverages. Qualifying luminaires shall be within 2 mounting heights of the hardscape area of outdoor dining. | Not applicable | 0.004 W/ft² | 0.030 W/ft² | 0.050 W/ft² | 0.075 W/ft2 |
Special Security Lighting for Retail Parking and Pedestrian Hardscape. This additional allowance is for illuminated retail parking and pedestrian hardscape identified as having special security needs. This allowance shall be in addition to the building entrance or exit allowance. | Not applicable | 0.004 W/ft² | 0.005 W/ft² | 0.010 W/ft² | No Allowance |
Security Camera. This additional allowance is for the illuminated general hardscape area. This allowance shall apply when a security camera is installed within 2 mounting heights of the general hardscape area and mounted more than 10 feet away from a building. | Not applicable | No Allowance | 0.018 W/ft² | 0.018 W/ft² | 0.018 W/ft² |
Ballast efficiency is the reference lamp power divided by the ballast input power when tested according to ANSI C82.6-2015.
The ratio of the output wattage to the input wattage is at 100 percent tubing load.
EXCEPTION to Section 170.2(e)7Bv: Single voltage external power supplies that are designed to convert 120 volt AC input into lower voltage DC or AC output, and have a nameplate output power less than or equal to 250 watts, shall comply with the applicable requirements of the Appliance Efficiency Regulations (Title 20).
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 170.2(e)7: Unfiltered incandescent lamps that are not part of an electronic message center (EMC), an internally illuminated sign, or an externally illuminated sign.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 170.2(e)7: Exit signs. Exit signs shall meet the requirements of the Appliance Efficiency Regulations.
kWPV = (CFA × A)/1000 + (NDU × B)
WHERE:
- kWPV = kWdc size of the PV system
- CFA = Conditioned floor area
- NDU = Number of dwelling units
- A = CFA adjustment factor from Table 170.2-T
- B = Dwelling unit adjustment factor from Table 170.2-T
Climate Zone | A - CFA | B - Dwelling Units |
1 | 0.793 | 1.27 |
2 | 0.621 | 1.22 |
3 | 0.628 | 1.12 |
4 | 0.586 | 1.21 |
5 | 0.585 | 1.06 |
6 | 0.594 | 1.23 |
7 | 0.572 | 1.15 |
8 | 0.586 | 1.37 |
9 | 0.613 | 1.36 |
10 | 0.627 | 1.41 |
11 | 0.836 | 1.44 |
12 | 0.613 | 1.40 |
13 | 0.894 | 1.51 |
14 | 0.741 | 1.26 |
15 | 1.56 | 1.47 |
16 | 0.59 | 1.22 |
kWPVdc = (CFA x A)/1000
WHERE:
- kWPVdc = Size of the PV system in kW.
- CFA = Conditioned floor area in square feet.
- A = PV capacity factor specified in Table 170.2-U for the building type
Where the building includes more than one of the space types listed in Table 170.2-U, the total PV system capacity for the building shall be determined by applying Equation 170.2-D to each of the listed space types and summing the capacities determined for each.
| Building Type |
Factor A – Minimum PV Capacity (W/ft² of conditioned floor area) Climate Zones 1, 3, 5, 16 |
Factor A – Minimum PV Capacity (W/ft² of conditioned floor area) Climate Zones 2, 4, 6-14 |
Factor A – Minimum PV Capacity (W/ft² of conditioned floor area) Climate Zone 15 |
| Grocery | 2.62 | 2.91 | 3.53 |
| High-Rise Multifamily | 1.82 | 2.21 | 2.77 |
| Office, Financial Institutions, Unleased Tenant Space | 2.59 | 3.13 | 3.80 |
| Retail | 2.62 | 2.91 | 3.53 |
| School | 1.27 | 1.63 | 2.46 |
| Warehouse | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.58 |
| Auditorium, Convention Center, Hotel/Motel, Library, Medical Office Building/Clinic, Restaurant, Theater | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.58 |
kWhbatt = kWPVdc x B / D0.5
WHERE:
- kWhbatt = Rated Useable Energy Capacity of the battery storage system in kWh
- kWPVdc = PV system capacity required by section 170.2(g) in kWdc
- B = Battery energy capacity factor specified in Table 170.2-V for the building type
- D = Rated single charge-discharge cycle AC to AC (round-trip) efficiency of the battery storage system.
kWbatt = kWPVdc x C
WHERE:
- kWbatt = Power capacity of the battery storage system in kWdc
- kWPVdc = PV system capacity required by section 170.2(g) in kWdc
- C = Battery power capacity factor specified in Table 170.2-V for the building type
Exception 1 to Section 170.2(h): No battery storage system is required if the installed PV system size is less than 15 percent of the size determined by Equation 170.2-D.
Exception 2 to Section 170.2(h): No battery storage system is required in buildings with battery storage system requirements with less than 10 kWh rated capacity.
| Factor B – Energy Capacity | Factor C – Power Capacity | |
| Storage-to-PV Ratio | Wh /W | W/W |
| Grocery | 1.03 | 0.26 |
| High -Rise Multifamily | 1.03 | 0.26 |
| Office, Financial Institutions, Unleased Tenant Space | 1.68 | 0.42 |
| Retail | 1.03 | 0.26 |
| School | 1.87 | 0.46 |
| Warehouse | 0.93 | 0.23 |
| Auditorium, Convention Center, Hotel/Motel, Library, Medical Office Building/Clinic, Restaurant, Theater | 0.93 | 0.23 |
Note: Authority: Sections 25213, 25218, 25218.5, 25402 and 25402.1, Public Resources Code. Reference: Sections 25007, 25008, 25218.5, 25310, 25402, 25402.1, 25402.4, 25402.8, and 25943, Public Resources Code.


